Inside This Issue: Clinical trial studies 3 mRNA HIV vaccine candidates; FDA authorizes second COVID-19 booster shots for some; funding opportunities; new COVID.gov website, and more.
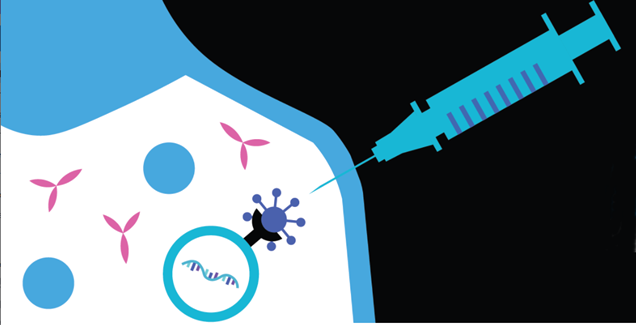
HIV Vaccine Development
NIAID Sponsors Clinical Trial to Study Three mRNA HIV Vaccine Candidates
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) is sponsoring a Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate three experimental HIV vaccines based on a messenger RNA (mRNA) platform – a technology used in several approved COVID-19 vaccines. The NIAID-funded HIV Vaccine Trials Network (HVTN), based at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, is conducting the trial. Vaccines using an mRNA platform work by delivering a piece of genetic material that instructs the body to make a protein fragment of a target pathogen such as HIV. The immune system then recognizes and remembers the protein, allowing it to mount a substantial immune response if a vaccinated person is later exposed to that pathogen.
HVTN 302 study researchers will evaluate whether the following three experimental HIV mRNA vaccines are safe and can induce an immune response: 1) BG505 MD39.3 mRNA; 2) BG505 MD39.3 gp151 mRNA; and 3) BG505 MD39.3 gp151 CD4KO mRNA. Each vaccine candidate is designed to present the spike protein found on the surface of HIV that facilitates the virus’s entry into human cells. Each HIV vaccine candidate encodes for different but highly related, stabilized proteins. None of the three vaccine candidates can cause HIV infection.
“Finding an HIV vaccine has proven to be a daunting scientific challenge,” notes NIAID Director Dr. Anthony Fauci. “With the success of safe and highly effective COVID-19 vaccines, we have an exciting opportunity to learn whether mRNA technology can achieve similar results against HIV infection.”
Participants in the study will receive one of the HIV vaccine candidates at doses of 100 mcg or 250 mcg, administered via intramuscular injections into the deltoid muscle. Participants will be evaluated for safety and immune responses through blood and lymph node fine-needle aspiration collection at specified times throughout the study. For more detailed information about the study, see this listing on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
COVID-19 Vaccination
FDA Authorizes Second COVID-19 Booster Dose for Older Persons and Those at Higher Risk for Severe Illness
On March 29, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 50 and older and for certain immunocompromised persons. The action follows the agency’s review of emerging evidence suggesting that a second booster dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine improves protection against severe COVID-19 and is not associated with new safety concerns.
The agency amended the emergency use authorizations for the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines as follows:
- A second booster dose of either vaccine may be given to persons aged 50 and older at least 4 months after they received their first booster dose of any authorized or approved COVID-19 vaccine.
- A second booster dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine may be given to persons 12 years of age and older with certain kinds of immunocompromise at least 4 months after they received their first booster dose of any authorized or approved COVID-19 vaccine. These are people who have undergone solid organ transplantation, or who are living with conditions that are considered to have an equivalent level of immunocompromise.
- A second booster dose of the Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine may be administered at least 4 months after the first booster dose of any authorized or approved COVID-19 vaccine to people 18 years and older with the same kinds of immunocompromise described above.
“Current evidence suggests some waning of protection over time against serious outcomes from COVID-19 in older and immunocompromised individuals,” noted Dr. Peter Marks, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. “Based on an analysis of emerging data, a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccine could help increase protection levels for these higher-risk individuals.”
Educational Resources
New HRSA Slide Decks Focus on RWHAP Clients and Health Outcomes
The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) has recently produced several slide decks that provide detailed information about all Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program (RWHAP) clients and older and transgender RWHAP clients, as well as viral suppression rates among RWHAP clients during 2020. These slide decks include the following:
Overview of clients served by RWHAP, 2020 – This slide deck presents information on the demographic characteristics, including selected social determinants of health, for all RWHAP clients in 2020. The slides include data breakdowns by gender, age, race/ethnicity, HIV transmission category, income level, housing status, and health insurance status.
Clients Aged 50 Years and Older Served by the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program, 2020 – This slide deck presents information on the demographic characteristics, included selected social determinants of health, for RWHAP clients aged 50 years and older. The slides include data breakdowns by gender, age, race/ethnicity, HIV transmission category, income level, and housing status.
Transgender Clients Served by the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program, 2020 – This slide deck presents information on the demographic characteristics, including selected social determinants of health, for RWHAP transgender clients. Slides include data breakdowns by gender, age, race/ethnicity, HIV transmission category, income level, housing status, and health insurance status. Additional detail is also provided on viral suppression among transgender RWHAP clients.
HIV Care Outcomes: Viral Suppression, 2020 – This slide deck presents information about trends in viral suppression rates among RWHAP clients during the period from 2010 through 2020. The slides include data breakdowns by gender, age, race/ethnicity, healthcare coverage, and housing status.
AIDSVu Highlights HIV/AIDS Among Native Americans
In recognition of National Native HIV/AIDS Awareness Day, AIDSVu has published a blog item and series of new infographics focusing on HIV/AIDS among American Indians, Alaska Natives, and Native Hawaiians. In 2020, 190 American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) people were diagnosed with HIV. During that year, gay and bisexual men accounted for 82% of new HIV diagnoses among AI/AN men, while injection drug use accounted for 43% of new HIV diagnoses among AI/AN women.
AIDSVu’s new infographics include the following:
- Trends in HIV Diagnoses Among AI/AN People
- New HIV Diagnoses Among AI/AN People, with Breakdowns by Sex and Transmission Category
- Breakdowns by Age of New HIV Diagnoses Among AI/AN People
- HIV Care Continuum Among AI/AN People
- States with Highest Number of New HIV Diagnoses Among AI/AN People
- Social Determinants of Health and HIV Among AI/AN People
For additional information on this topic, you can visit NEAETC’s Online HIV Resource Library page focusing on American Indians & Alaska Natives and HIV.

Funding Opportunities
CDC Issues $50-Million Funding Opportunity to Strengthen Syringe Services Programs
CDC recently issued the Strengthening Syringe Services Programs funding opportunity (NOFO# CDC-RFA-PS22-2208), which aims to increase access to harm reduction services for people who currently inject, or have a history of injecting, drugs, and to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases and other complications of injection drug use. The NOFO has two components. “Component 1 will expand a national network of syringe services programs (SSPs) to facilitate communication among SSPs, other harm reduction programs, and trusted national organizations with a demonstrated portfolio in improving the health of persons who use drugs,” according to CDC. “Component 2 will increase support and resources to SSPs for implementation of syringe distribution and disposal; testing, treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases and infectious complications from injection drug use; and mitigation of other harms due to drug use.” CDC expects to award a total of $50 million to two grantees. The application deadline is May 2.
SAMHSA Funding Opportunities to Provide Mental Health and Substance Use Services for People at Risk for or Living with HIV
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) recently issued three Notices of Funding Opportunities (NOFOs) totaling nearly $44 million to strengthen mental health and substance use services for individuals at risk for or living with HIV/AIDS. The purpose of Minority AIDS Initiative – Service Integration (SM-22-005) “is to provide resources to help reduce the co-occurring epidemics of HIV, hepatitis, and mental health disorders through accessible, evidence-based, culturally appropriate mental and co-occurring disorder treatment that is integrated with HIV primary care and prevention services.” This grant will provide a total of $8.7 million over a four-year period to as many as 18 grantees. The application due date is April 25.
The purpose of Substance Use Disorder Treatment for Racial Ethnic/Minority Populations at High Risk for HIV/AIDS (NOFO# TI-22-004) “is to increase engagement in care for racial and ethnic underrepresented individuals with substance use disorders and/or co-occurring substance use and mental disorders who are at risk for or living with HIV/AIDS and receive HIV/AIDS services/treatment.” This grant will provide up to $30.5 million in funding over a five-year period to as many as 61 grantees. The application due date is April 29.
The purpose of Substance Abuse and HIV Prevention Navigator Program for Racial Ethnic Minorities (NOFO# SP-22-002) “is to provide substance misuse and HIV prevention services to racial/ethnic minority males at risk for HIV/AIDS. The program will place an emphasis on males who have sex with other males, including transgender individuals, as well as those who identify as LGBTQ+ who are not in stable housing and reside in communities with high incidence rates of HIV.” This grant will provide a total of up to $4.5 million in funding over a five-year period to as many as 18 grantees. The application deadline is May 2.
Other COVID-19 News
White House Announces Launch of Comprehensive COVID.gov Website
Late last month, the White House announced the launch of the COVID.gov website, which is designed to be a “one-stop-shop” website to help all people in the U.S. gain greater access to protective face masks; COVID-19 vaccines, tests, and treatments; and the latest updates about COVID-19 in their area. “As part of COVID.gov, a new Test-to-Treat locator will help people access the more than 2,000 pharmacies and community health centers across the country where COVID-19 tests and treatments are available for those who need them.
The COVID.gov website is available in English, Spanish, and simplified Chinese and is also accessible for persons using assistive technologies. The Administration is also making all of these COVID-19 tools available by phone through a national hotline at (800) 232-0233 [TTY: (888) 720-7489], which supports over 150 languages. For people with disabilities who may need additional support, the Disability Information and Access Line (DIAL) is also available at (888) 677-1199 or via email at: DIAL@usaginganddisability.org.
Recent Summaries and Research Reports
CDC’s COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review highlights key data from its COVID Data Tracker, narrative interpretations of the data, and visualizations from the week. Themes of recent Weekly Review issues include the added protection from a second booster dose, COVID-19 wastewater surveillance, benefits of vaccine boosting.
The Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) is also providing continuing coverage of COVID-19-related research. CDC is archiving its MMWR reports on a page devoted to studies about COVID-19. For your convenience, we have compiled below links to recent MMWR papers:
Use of At-Home COVID-19 Tests – United States, August 23, 2021-March 12, 2022



.jpg)

