Insdie This Issue: FDA authorizes Moderna vaccine and over-the-counter COVID-19 test, falling death rates among persons with HIV, record viral suppression among Ryan White clients, and new HIV, substance use, and mental health guide.
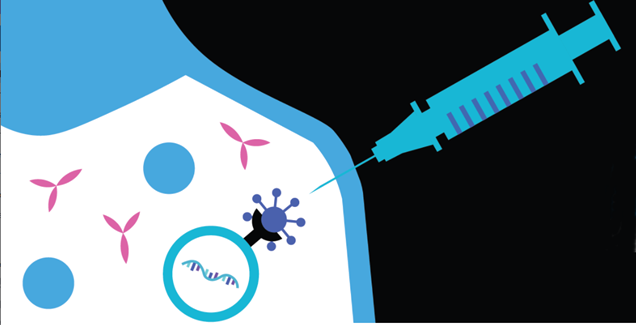
COVID-19 Vaccines and Tests
FDA Issues EUA for Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine
On December 18, just one week after granting an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an EUA for a second vaccine – the Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine. The EUA allows the Moderna Vaccine to be distributed in the U.S. for use in persons aged 18 years and older.
Both FDA-authorized vaccines were highly effective in preventing COVID-19 in clinical trials, and incorporate a small piece of genetic material called mRNA derived from the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is responsible for COVID-19. This mRNA viral fragment instructs cells in the body to make the virus’s distinctive “spike” protein. When people receive these vaccines, their bodies produce copies of the spike protein, which does not cause disease, but triggers the immune system to learn to react defensively, producing an immune response against SARS-CoV-2.
“With the availability of two vaccines now for the prevention of COVID-19, the FDA has taken another crucial step in the fight against this global pandemic that is causing vast numbers of hospitalizations and deaths in the U.S. each day,” noted FDA Commissioner Dr. Stephen Hahn. As of December 20, the total recorded cases of COVID-19 reached about 77.3 million worldwide, with over 18.0 million in the U.S., according to the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Total deaths from COVID-19 reached 1.7 million globally, with over 319,000 in the United States.
First OTC, Fully At-Home Diagnostic Test for COVID-19 Authorized by FDA
The FDA also recently issued an EUA for the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test – the first over-the-counter (OTC), fully at-home diagnostic test for COVID-19. The test, which is authorized for use in persons aged 2 years or older, detects fragments of proteins of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from a nasal swab sample. “Today’s authorization is a major milestone in diagnostic testing for COVID-19,” noted FDA’s Dr. Hahn. “By authorizing a test for over-the-counter use, the FDA allows it to be sold in places like drug stores, where a patient can buy it, swab their nose, run the test, and find out their results in as little as 20 minutes.” Options for COVID-19 testing are expanding rapidly. The FDA has authorized more than 225 diagnostic tests for COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic, including more than 25 tests that allow for home collection of samples, which are then sent to a lab for testing.
Mortality in Persons with HIV
U.S. HIV-Related Deaths Fell by Nearly Half from 2010 to 2017
Advances in early HIV diagnosis, linkage to treatment, and sustained access to high-quality care and treatment have led to substantial reductions in both overall and HIV-related death rates among persons with diagnosed HIV (PWDH), according to a recent study from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In the study, CDC researchers analyzed U.S. HIV surveillance data to assess progress toward reducing deaths among PWDH aged 13 years or older. They calculated the age-adjusted death rates per 1,000 PWDH, and also classified deaths as HIV-related or non-HIV-related when information on the underlying cause of death was available.
From 2010 through 2018, overall death rates decreased by nearly 37%, from 19.4 to 12.3 per 1,000 PWDH, according to the CDC team. During 2010 through 2017, HIV-related death rates decreased over 48% (from 9.1 to 4.7), while non-HIV-related death rates decreased about 9% (from 9.3 to 8.5).
“Despite success in reducing rates of HIV-related deaths among PWDH, differences still exist by gender, race/ethnicity, age, transmission category, and region,” the CDC team noted. In 2017, rates of HIV-related deaths per 1,000 PWDH were highest among persons of multiple races (7.0) and Black/African American persons (5.6), followed by White persons (3.9) and Hispanic/Latino persons (3.9). The HIV-related death rate was highest in the South (6.0) and lowest in the Northeast (3.2). HIV-related death rates were also higher among females (5.4) than males (4.5) and transgender females (4.3).
“Variation in timely diagnosis and treatment initiation, along with ongoing treatment, likely contributes to differences in HIV-related deaths,” according to the report. “Higher levels of poverty, unemployment, and persons uninsured, challenges associated with accessing care, and HIV-related stigma likely affect timely diagnosis and access to treatment and contribute to higher rates of HIV-related deaths. Expanded efforts to address these and other structural barriers are critical to improving health outcomes, including reducing differences in HIV-related death rates, especially among Black persons and persons in the South.”
Continuum of HIV Care
HRSA: Record High Viral Suppression Rates Among RWHAP Clients in 2019
HIV viral suppression rates reached a record high of 88.1% last year among clients receiving medical care through the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program (RWHAP), according to the latest RWHAP Annual Client-Level Data Report for 2019. The 145-page report, published by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) gives an in-depth review of demographic and socioeconomic information for RWHAP clients. It includes breakdowns by age, race/ethnicity, transmission risk category, federal poverty level, healthcare coverage, and housing status. In addition, the report provides focused analyses to measure RWHAP's progress toward achieving selected HIV-related health outcomes. Selected highlights of the report are summarized below.
Demographic Characteristics
- The RWHAP served approximately 568,000 clients during 2019, an increase of about 34,000 from 2018.
- The percentage of RWHAP clients in the 5-year age groups between 40 and 54 years old decreased, while those older than 55 years increased. The percentage of clients 55 years and older rose from 25.5% in 2015 to 32.8% in 2019.
- Nearly three-quarters of RWHAP clients were from racial/ethnic minority populations. Last year, 46.6% of clients self-identified as Black/African American, 23.3% as Hispanic/Latino, and less than 2% each as American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and persons of multiple races. Whites accounted for 26.6% of clients.
- The majority of RWHAP clients (71.6%) were male. In 2019, 26.2% were female and 2.3% were transgender.
- Selected demographic data on RWHAP clients are summarized in this infographic.
Retention in Care and Viral Suppression
- The percentages of RWHAP clients who were retained in HIV care were fairly stable from 2015 through 2019 - when 80.8% of clients who had received at least one outpatient ambulatory health services (OAHS) visit were retained in care.
- A few subpopulation groups had substantially lower retention-in-care rates: American Indian/Alaska Natives (74.8%); clients aged 20-24 years (75.4%), 25-29 years (74.3%), and 30-34 years (75.3%); transgender clients with HIV attributed to sexual contact and injection drug use (75.4%); clients with Veterans Administration (73.3%) and Indian Health Service (66.0%) health care coverages; and clients with temporary or unstable housing (75.5% and 73.4%, respectively).
- Viral suppression rates rose from 83.4% in 2015 to 88.1% overall among RWHAP with at least one OAHS visit. Young people 15-19 and 20-24 years old showed the greatest improvements in viral suppression during the period, rising nearly 11% to 79.5% and 79.1% respectively. Viral suppression rates among transgender women also rose substantially, from 77.0% to 82.9%.

Substance Use, Mental Disorders, and HIV
New Guide Focuses on HIV Among People Living with Substance Use and Mental Disorders
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has published a new 70-page guide that reviews HIV prevention and treatment interventions for people living with substance use and mental disorders who are at risk for, or living with, HIV. The interventions discussed include: practices to increase uptake of, and improve adherence to, pre-exposure prophylaxis;
syringe services programs; contingency management; cognitive behavioral therapy; and patient navigation services.
For each of these interventions, the guide provides a review of the available evidence, including:
- the outcomes achieved, such as reducing the risk of acquiring HIV infection or increasing linkage to and retention in HIV care;
- the practitioners who delivered the interventions, such as behavioral health practitioners, pharmacy staff, health educators, or community members; and
- the settings in which the interventions were implemented, such as medical care settings, behavioral health treatment settings, substance use treatment settings, and community settings.
The guide also includes a section with examples of effective programs and strategies, as well as a summary of available resources for program evaluation and quality improvement.
%20small.jpg)
HIV Educational Resources
Data on State-Level HIV Care Continuum & Social Determinants Added to AIDSVu
Emory University updated its AIDSVu interactive online mapping tool this month to incorporate HIV care continuum data at the state level, as well as new maps of related infectious diseases and additional social determinants of health indicators. AIDSVu now includes extensive national, state, county, and city-level data, with demographic breakdowns for HIV prevalence, testing, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) needs and use, new HIV diagnoses, late HIV diagnoses, linkage to care, and HIV mortality. The added social determinants of health indicators are unemployment, housing, food security, and Medicaid expansion.
“These data come during a time of public health crisis as our nation and the world fight to control the COVID-19 pandemic – and as the challenges of our national healthcare system come into the spotlight,” noted Emory’s Patrick Sullivan, principal scientist for AIDSVu. “It is our hope these new interactive maps and visualizations can help the HIV community showcase the close link between disparities in HIV outcomes – especially among racial and ethnic groups – and access to basic human needs like employment, food, and housing.”
New and Updated Fact Sheets, Issue Brief, and Guides from CDC
HIV in the United States and Dependent Areas – This visually rich, two-page fact sheet summarizes key statistics for 2018, including: new HIV diagnoses, HIV prevalence, and the continuum of HIV care. For HIV diagnoses, breakdowns and trends from 2014 through 2018 are provided for selected transmission categories, race/ethnicities, genders, and ages.
HIV and Men – This fact sheet summarizes data on new HIV diagnoses among U.S. men, with breakdowns by transmission category, including male-to-male sexual contact, heterosexual contact, injection drug use (IDU), as well as the combination of male-to-male sexual contact and IDU. Information is also provided on HIV prevalence, the HIV care continuum, and trends in new diagnoses over time.
Diagnose and Treat to Save Lives: Decreasing Deaths Among People with HIV – This two-page fact sheet summarizes the latest statistics and trends on all-cause deaths and HIV-related deaths among persons with HIV. It also includes information on racial/ethnic and regional disparities in death rates, as well as steps healthcare providers, health departments, and individuals can take to improve health outcomes and save lives.
Evidence of HIV Treatment and Viral Suppression in Preventing Sexual Transmission of HIV – This issue brief provides a concise summary of the evidence, complete with citations to clinical trials updated through 2020. It also provides information on maximizing the effectiveness of HIV prevention strategies in clinical practice.
HIV Treatment Is Prevention Pocket Guide – This easy-to-read resource is arranged into four sections focusing on what HIV treatment is, when to start, options for HIV prevention, and maintaining an undetectable viral load.
PEP Pocket Guide – Similar in format to the treatment guide above, this resource for consumers includes sections on what HIV post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is, determining whether it is right for you, how to use PEP effectively, and ways to cover the costs of PEP.
.jpeg)
COVID-19 Research
Recent COVID-19 Studies in MMWR
CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) is continuing its extensive coverage of COVID-19-related research. The reports are aggregated on a page devoted to studies about COVID-19, and summarized in a weekly podcast. Recent reports include:
- The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ Interim Recommendation for Use of Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine — United States, December 2020
- Health Center Testing for SARS-CoV-2 During the COVID-19 Pandemic – United States, June 5-October 2, 2020
- Telehealth Practice Among Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic – United States, July 11-17, 2020
- Factors That Might Affect SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Among Foreign-Born and U.S.-Born Poultry Facility Workers – Maryland, May 2020
- Estimated Resource Costs for Implementation of CDC’s Recommended COVID-19 Mitigation Strategies in Pre-Kindergarten through Grade 12 Public Schools – United States, 2020-21 School Year
- Factors Associated with Positive SARS-CoV-2 Test Results in Outpatient Health Facilities and Emergency Departments Among Children and Adolescents Aged <18 Years – Mississippi, September-November 2020



.png)
%20small.jpg)